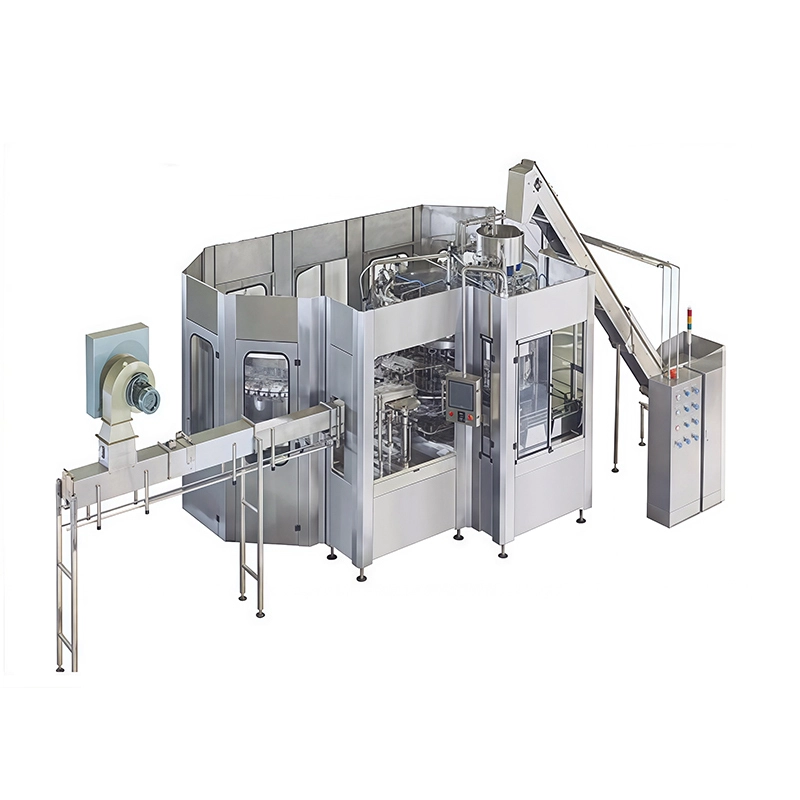
Hot Filling Machine
Key Features and Benefits:
● The hot filling process is engineered to handle high temperatures with precision and efficiency, offering distinct advantages for product preservation and packaging integrity.
● Hot filling machines are built for high-output production lines, with speed directly influenced by the bottle's size and shape.
Core Functionality and Key Features
The hot filling process is engineered to handle high temperatures with precision and efficiency, offering distinct advantages for product preservation and packaging integrity.
The process begins with the product being heated to the target temperature in an integrated pasteurizer or heater and held for a specific time to ensure microbial elimination. The hot liquid is then filled into containers, which are immediately sealed. The key step follows immediately after sealing: the filled and sealed bottles are conveyed through a cooling tunnel. Here, they are gradually cooled with water sprays. This controlled cooling is vital as it treats the container, using the residual heat to pasteurize the bottle's inner surface and, for PET bottles, induces slight shrinkage to create a secure, vacuum-tight seal upon cooling. This "vacuum panel" design in hot-fill PET bottles is a direct result of this process.
Modern hot fillers are constructed with corrosion-resistant, food-grade stainless steel (SUS304/316L) to withstand constant exposure to heat and acidic products. They feature temperature control systems to maintain precise fill temperatures and are often equipped with CIP (Cleaning-In-Place) systems for thorough and efficient sanitation. To handle the hot liquids, they utilize specialized, heat-resistant filling valves designed to prevent dripping and ensure accuracy.
Production Capacity and Versatility
Hot filling machines are built for high-output production lines, with speed directly influenced by the bottle's size and shape.
● Production Output: The hourly capacity of a hot filling line is highly adaptable. For smaller, single-serve bottles (e.g., 250ml to 500ml), modern rotary hot fillers can achieve very high speeds, reaching up to 36,000 bottles per hour (BPH). For larger, family-size bottles (e.g., 1L to 2L), the output is accordingly lower but still robust, typically ranging from 3,000 to 12,000 BPH.
● Compatible Containers: These machines are versatile in handling different container types. They are primarily used with heat-resistant PET bottles that are specifically designed with vacuum panels to absorb the negative pressure created during cooling. They can also fill glass bottles and various types of jars, which are naturally capable of withstanding the thermal process.
Machine Display
Primary Applications
Hot filling technology is predominantly used for high-acid (pH below 4.6) beverages and liquid foods where the heat treatment effectively ensures microbial stability. Its primary applications include:
● Juices and Nectars: Such as orange, apple, grape, and tomato juice, preserving a fresh-squeezed flavor profile.
● Tea and Coffee Drinks: Including ready-to-drink (RTD) teas and canned coffee beverages.
● Functional and Sports Beverages: For products that may be sensitive to other preservation methods.
● Other Liquid Foods: This includes products like jams, sauces, and syrups.
By integrating pasteurization and filling into a single, automated process, a hot filling machine provides manufacturers with a reliable, cost-effective solution for producing shelf-stable, high-quality beverages that are favored by markets worldwide.
FAQ
Customer Review
Discover what our clients have to say